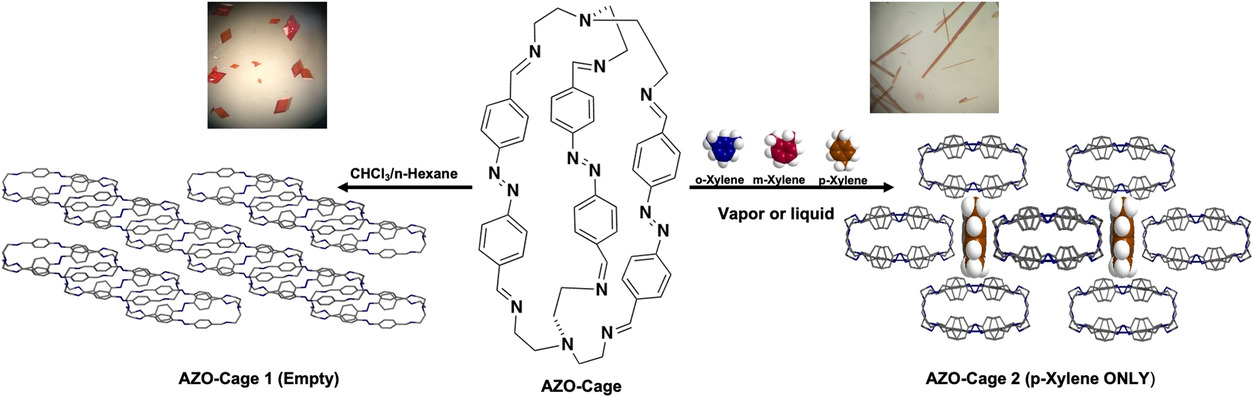
B. Moosa, L. Alimi, A. Shkurenko, A. Fakim, G. Zhang, K. N. Salama & M. Eddaoudi, N. Khashab. A polymorphic azobenzene cage for energy efficient and highly selective p‐Xylene separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10.1002/anie.202007782
Developing the competency of molecular sorbents for energy‐saving applications, such as C8 separations, requires efficient, stable, scalable and easily recyclable materials that can readily transition to commercial implementation. Here, we report an azobenzene‐based cage for the selective separation of p ‐xylene isomer across a range of C8 isomers in both vapor and liquid states with selectivity that is higher than the reported all‐organic sorbents. Interestingly, the crystal structure shows non‐porous cages that are separated by p‐ xylene molecules through selective CH… p interactions between the azo bonds and the methyl hydrogens of the xylene molecules. This cage is stable in solution and can be regenerated directly under vacuum to be used in multiple cycles. We envisage that this work will promote the investigation of the azo bond as well as guest induced crystal to crystal phase transition in non‐porous organic solids for pivotal energy-intensive separations.