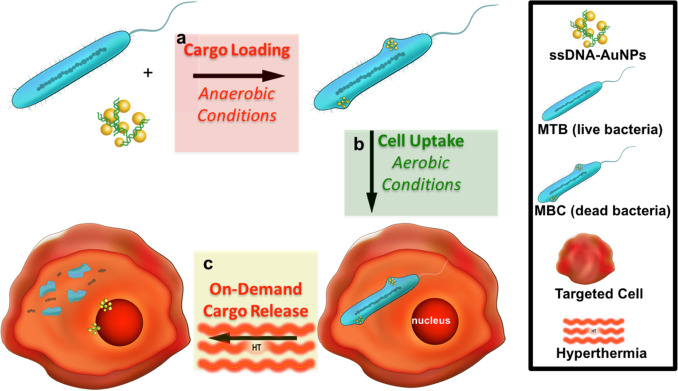
In spite of the huge advances in the area of synthetic carriers, their efficiency still poorly compares to natural vectors. Herein, we report the use of unmodified magnetotactic bacteria as a guidable delivery vehicle for DNA functionalized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). High cargo loading is established under anaerobic conditions (bacteria is alive) through endocytosis where AuNPs are employed as transmembrane proteins mimics (facilitate endocytosis) as well as imaging agents to verify and quantify loading and release. The naturally bio-mineralized magnetosomes, within the bacteria, induce heat generation inside bacteria through magnetic hyperthermia. Most importantly after exposing the system to air (bacteria is dead) the cell wall stays intact providing an efficient bacterial vessel. Upon incubation with THP-1 cells, the magnetotactic bacterial cages (MBCs) adhere to the cell wall and are directly engulfed through the phagocytic activity of these cells. Applying magnetic hyperthermia leads to the dissociation of the bacterial microcarrier and eventual release of cargo.