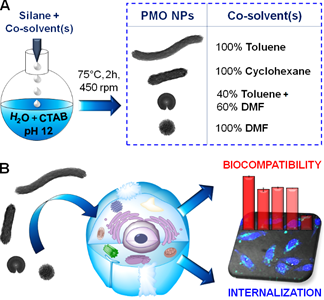
In this work, we describe the sol-gel syntheses of para-substituted phenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) nanoparticles (NPs) with tunable morphologies from nanowires to nanospheres. Our findings showed the key role of the addition of organic co-solvents in the aqueous templates on the final morphologies of PMO NPs. Other factors such as the temperature, the stirring speed, and the amount of organic solvents also influence the shape of PMO NPs. The tuning of the shape of the PMO nanomaterials allowed us to study the influence of the particle morphology on the cellular internalization and biocompatibility.