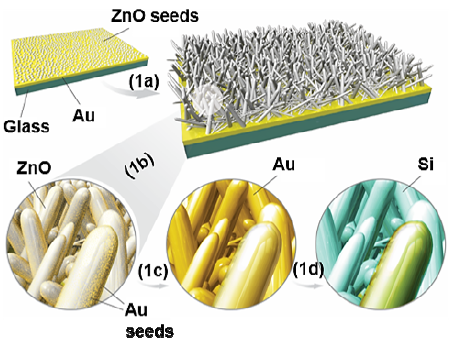
Low limit detection and quantification of heavily used aromatic compounds is critical for industries as well as environmental and healthcare protection. In this study, semiconductor/noble metal nanostructures are fabricated as SERS-active substrates for analytical and quantitative detection of xylene isomers. These substrates are composed of a standing array of zinc oxide/gold core-shell structures encapsulated by a silica coating. Their performance is verified by obtaining the composition of xylene isomers in a xylene histological grade sample and compared to gas chromatography (GC) data, which showed a mere 2.9% error for o-xylene and 3.7% error for m, p-xylene. The detection limit of this substrate is 14 ppm for o,m-xylene and 35 ppm for p-xylene.