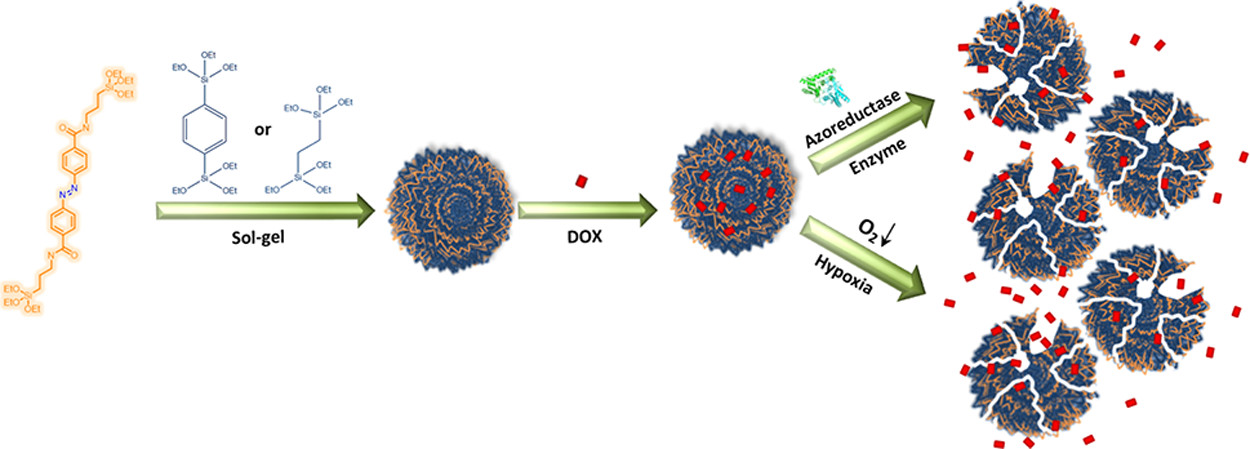
Porous materials with molecular-scale ordering have attracted major attention mainly because of the possibility to engineer their pores for selective applications. Periodic mesoporous organosilica is a class of hybrid materials where self-assembly of the organic linkers provides a crystal-like pore wall. However, unlike metal coordination, specific geometries cannot be predicted because of the competitive and dynamic nature of noncovalent interactions. Herein, we study the influence of competing noncovalent interactions in the pore walls on the biodegradation of organosilica frameworks for drug delivery application. These results support the importance of studying self-assembly patterns in hybrid frameworks to better engineer the next generation of dynamic or “soft” porous materials.