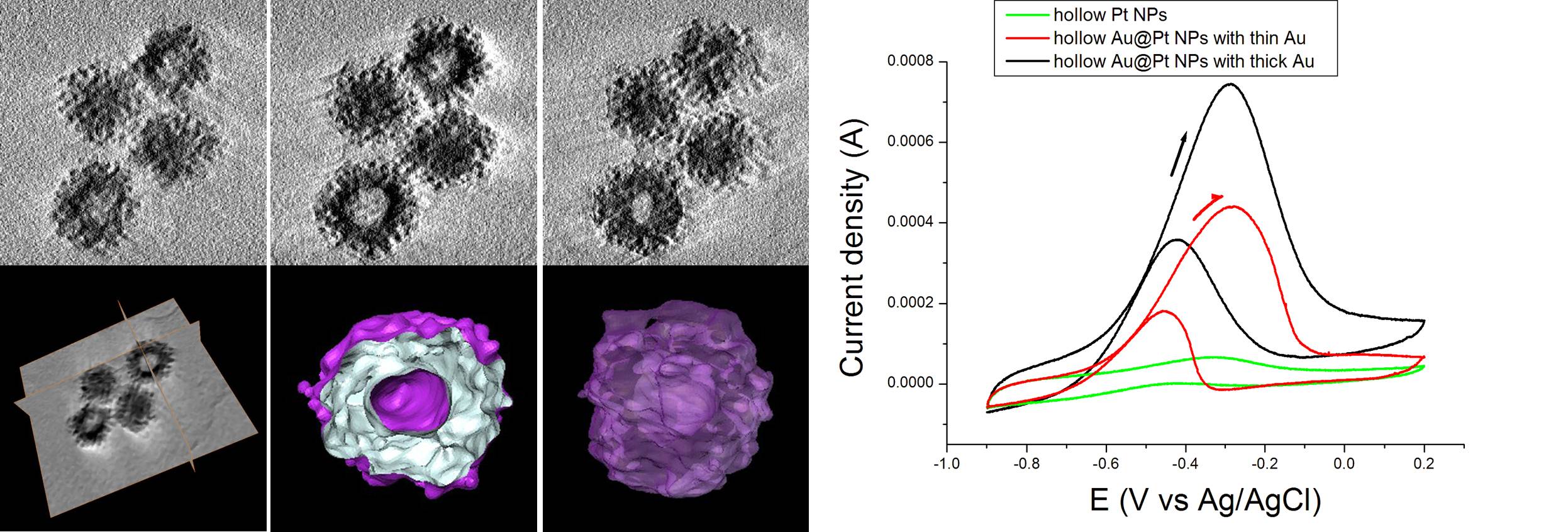
Hybrid alloys among gold, palladium and platinum become a new category of catalysts primarily due to their enhanced catalytic effects. Enhancement means not only the effectiveness, but also the uniqueness as catalysts for the reactions that individual metals may not catalyze. Here, one-step preparation of hollow Au@Pd and Au@Pt alloy core-shell nanoparticles (NPs) and their use as electrocatalysts are reported. Galvanic displacement with Ag NPs is used to obtain hollow NPs, and higher reduction potential of Au compared to Ag, Pd, and Pt helps to produce hollow Au cores first, followed by Pd or Pt shell growth. Continuous and highly crystalline shell growth was observed in Au@Pd core-shell NPs, but sporadic and porous-like structure was observed in Au@Pt core-shell NPs. Along with alloy NPs, hollow Au and Pt NPs are also prepared. Twin boundaries which typically observed in large size (> 20 nm) Au NPs were not observed in hollow Au NPs. This absence is believed due to the role of the hollows, which significantly reduce the strain energy of edges where the two lattice planes meet. In ethanol oxidation reactions in alkaline medium, Au@Pd core-shell NPs show the best catalytic activity. Hollow Au@Pt core-shell NPs maintain higher current density than hollow Pt, which is thought due to the better crystallinity of Pt shell as well as the alloyed effect of Au cores.