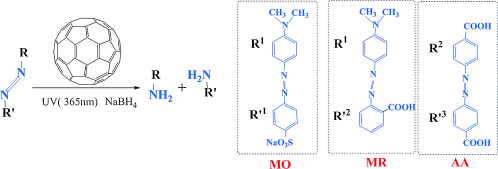
Metal-free fullerene (C60) was found to be an effective catalyst for the reduction of azo groups in basic aqueous solution under UV irradiation in the presence of NaBH4. Use of NaBH4 by itself is not sufficient to reduce the azo dyes without the assistance of a metal catalyst such as Pd and Ag. Experimental and theoretical results suggest that C60 catalyzes this reaction by using its vacant orbital to accept the electron in the bonding orbital of azo dyes, which leads to the activation of the N[DOUBLE BOND]N bond. UV irradiation increases the ability of C60 to interact with electron-donor moieties in azo dyes.