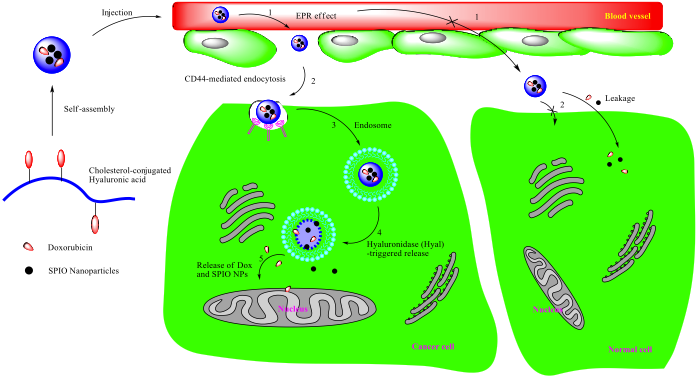
Tumor targetability and stimuli responsivity of drug delivery systems (DDS) are key factors in cancer therapy. Implementation of multifunctional DDS can afford targetability and responsivity at the same time. Herein, cholesterol molecules (Ch) were coupled to hyaluronic acid (HA) backbones to afford amphiphilic conjugates that can self-assemble into stable micelles. Doxorubicin (DOX), an anticancer drug, and superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles (NPs), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents, were encapsulated by Ch–HA micelles and were selectively released in the presence of hyaluronidase (Hyals) enzyme. Cytotoxicity and cell uptake studies were done using three cancer cell lines (HeLa, HepG2 and MCF7) and one normal cell line (WI38). Higher Ch–HA micelles uptake was seen in cancer cells versus normal cells. Consequently, DOX release was elevated in cancer cells causing higher cytotoxicity and enhanced cell death.